Laser-based SEE (Single Event Effect) evaluation is a practical alternative method to heavy ion beam testing for analyzing the radiation hardness of semiconductors. It is actively utilized in countries such as the United States, China, and Russia. Among these, the United States provides notable application cases.
In the U.S., various radiation evaluations using lasers are conducted in NASA-affiliated research institutions. Laser-based SEE testing is gaining attention for its fast evaluation speed and precise detection of vulnerabilities. With lasers, sensitive areas in circuits can be accurately pinpointed, enabling early identification of SEE vulnerabilities during the initial design stages.
The official guideline document, NASA/TM–20205011579, outlines recommendations for the use of COTS EEE parts in NASA missions. It explicitly mentions laser-based evaluation as one of the key methods for SEE assessment. This document lists picosecond laser evaluation, heavy ion and proton testing, and Cf-252 screening among its suggested SEE evaluation techniques. Notably, laser-based radiation hardness testing is presented before traditional radiation sources, indicating its efficiency in COTS component evaluations.

Recommendations on Use of Commercial-Off-The-Shelf (COTS) Electrical, Electronic, and Electromechanical (EEE) Parts for NASA Missions
Reference: NASA Engineering and Safety Center. (2020). Recommendations on use of commercial-off-the-shelf (COTS) electrical, electronic, and electromechanical (EEE) parts for NASA missions (NASA/TM–20205011579, NESC-RP-19-01490). Langley Research Center.
Additionally, the MEAL (Mission, Environment, Application, Lifetime) guidelines (NASA/TM–2018-220074) also identify laser-based SEE evaluation as one of the radiation test methods. These guidelines emphasize the cost-effectiveness and shorter evaluation times of laser testing compared to proton or heavy ion beam testing. Furthermore, they state that laser evaluations offer complementary insights to those obtained from heavy ion testing.
Laser evaluation is highly effective in the early-stage identification of circuit vulnerabilities and is recommended for use in radiation hardness design studies or complex high-density circuit assessments.
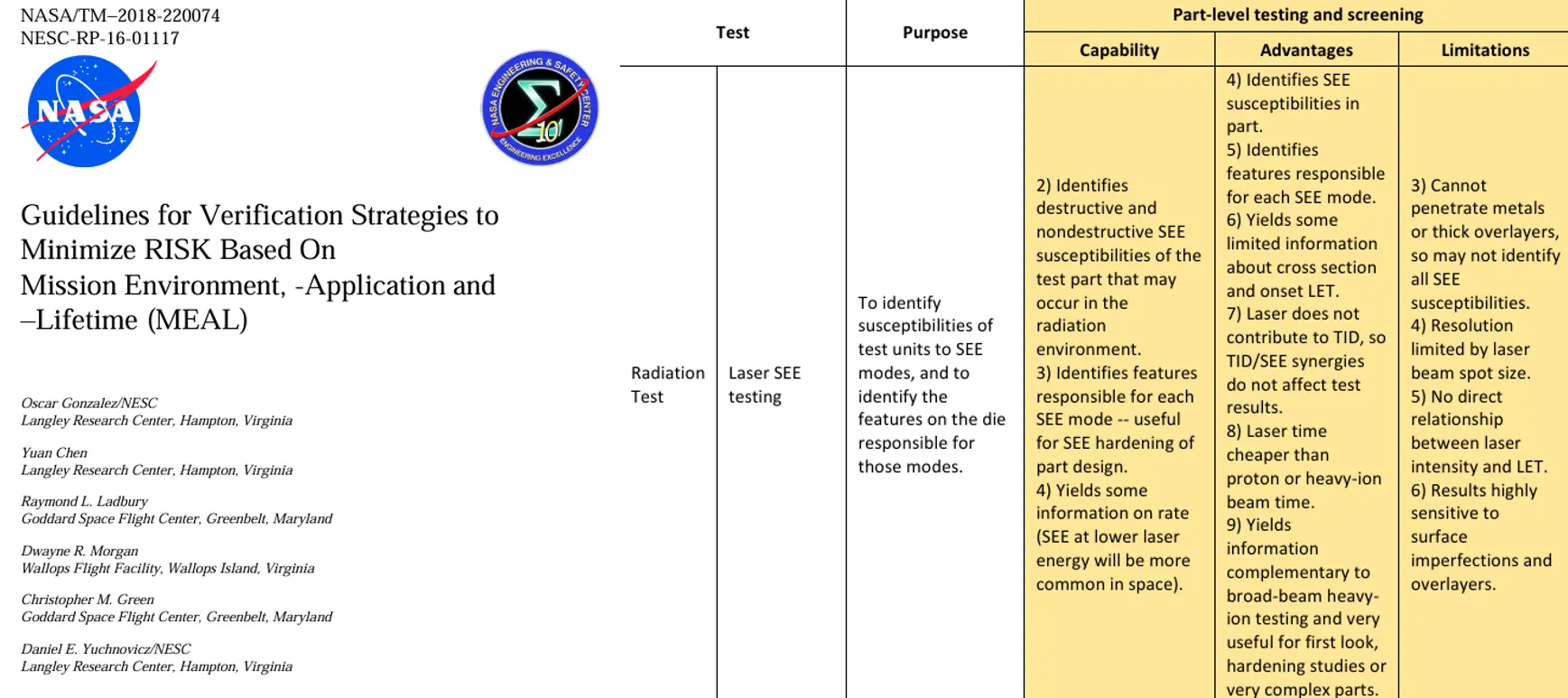
Guidelines for Verification Strategies to Minimize RISK Based on Mission Environment, Application, and Lifetime (MEAL)
Reference: NASA, Guidelines for Verification Strategies to Minimize RISK Based on Mission Environment, Application and Lifetime (MEAL), NASA/TM–2018-220074, June 2018.
At QRT, we are developing laser evaluation technology in line with these international trends. By analyzing the correlation between laser energy and LET (Linear Energy Transfer), we conduct evaluations that predict heavy ion test results and identify SEE vulnerabilities within components with high precision.
Related Articles


