What is a Heavy-Ion Beam?
The diagram below shows several types of radiation particles and compares their relative masses. Taking the mass of a proton or neutron as 1, the electron’s relative mass is approximately 1/1,836. Although the electron is drawn disproportionately large for clarity, the illustration conveys the orders-of-magnitude difference between electrons and nucleons.
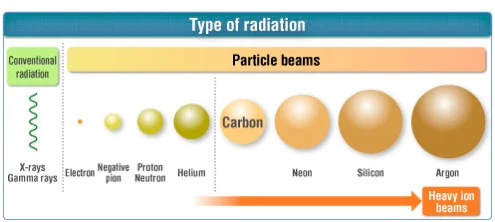
Relative size of radiation particles
|
Source: Medical Excellence JAPAN
The nucleus of a helium atom is called an alpha particle.
In radiation-effects work, heavy ions generally refer to ions heavier than helium (atomic number Z ≥ 3), while electrons, protons, and helium nuclei are treated separately.
Radiation in space appears either as electromagnetic waves or as particles.
A particle beam is a collimated stream of accelerated particles (e.g., electrons, protons, ions, or neutrons).
When the beam consists of ions heavier than helium, it is specifically termed a heavy-ion beam.
Accelerators are categorized by the type of particle they accelerate. For example, electron accelerators and proton accelerators accelerate electrons and protons, respectively, to near the speed of light. These accelerators are primarily used to accelerate particles of relatively light elements like helium or carbon.
In contrast, heavy ion accelerators are used to accelerate ions heavier than helium, such as xenon (Xe), to synthesize new atomic nuclei or study the properties of materials.
Since neutrons are particles with no electric charge, they cannot be directly accelerated using conventional accelerator technologies that rely on electric or magnetic fields. Therefore, indirect methods are used to obtain a neutron beam. The most common method is to collide accelerated high-energy protons or electrons with a specific target material. This collision process, known as a spallation reaction, releases a large number of neutrons.
Other methods for obtaining neutrons include nuclear fission or nuclear fusion reactions that occur within nuclear reactors, or inducing specific nuclear reactions to produce neutrons. The neutron beams created this way are used for various purposes, such as studying material structures or in the medical field.


